Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
"In the garment industry, stories about workers who barely eke out an existence on 'starvation wages' are legion: Factory workers in New Delhi often describe living in makeshift hovels 'barely fit for animals.' A young woman from Myanmar might wrestle with the decision to feed her children or send them to school. In Bangladesh, sewing-machine operators frequently toil for 100 hours or more a week, only to run out of money before the end of the month. Workers have demanded higher pay in all those countries, of course, sometimes precipitating violence between protesters and police. Companies in general, however, have preferred to sidestep the issue altogether. In fact, no multinational brand or retailer currently claims to pay its garment workers a wage they can subsist on."
Via FCHSAPGEO
"In the 2016 edition of its World Development Indicators, the World Bank has made a big choice: It’s no longer distinguishing between 'developed' countries and “developing” ones in the presentation of its data. The change marks an evolution in thinking about the geographic distribution of poverty and prosperity. But it sounds less radical when you consider that nobody has ever agreed on a definition for these terms in the first place. The International Monetary Fund says its own distinction between advanced and emerging market economies “is not based on strict criteria, economic or otherwise.” The United Nations doesn’t have an official definition of a developing country, despite slapping the label on 159 nations. And the World Bank itself had previously simply lumped countries in the bottom two-thirds of gross national income (GNI) into the category, but even that comparatively strict cut-off wasn’t very useful."
Marketplace® is your liaison between economics and life. Noted for timely, relevant and accessible coverage of business news across both audio and digital platforms, Marketplace programs are heard by more than 14 million weekly listeners. This makes the Marketplace portfolio the most widely heard business or economic programming in the country.
Via EmilyCoop
Avocados have become a super trendy food, but few of us know how they're even grown or harvested. We visit a California farm to uncover the amazing story of the avocado — and share the secrets to choosing, ripening and cutting the fruit.
Via Dawn Haas Tache
What economists around the world get wrong about the future. The idea that economic growth can continue forever on a finite planet is the unifying faith of industrial civilization. That it is nonsensical in the extreme, a deluded fantasy, doesn't appear to bother us. We hear the holy truth in the decrees of elected officials, in the laments of economists about flagging GDP, in the authoritative pages of opinion, in the whirligig of advertising, at the World Bank and on Wall Street, in the prospectuses of globe-spanning corporations and in the halls of the smallest small-town chambers of commerce. Growth is sacrosanct. Growth will bring jobs and income, which allow us entry into the state of grace known as affluence, which permits us to consume more, providing more jobs for more people producing more goods and services so that the all-mighty economy can continue to grow. "Growth is our idol, our golden calf," Herman Daly, an economist known for his anti-growth heresies, told me recently. Tags: op-ed, economic, industry, sustainability, development, consumption, climate change, environment, resources.
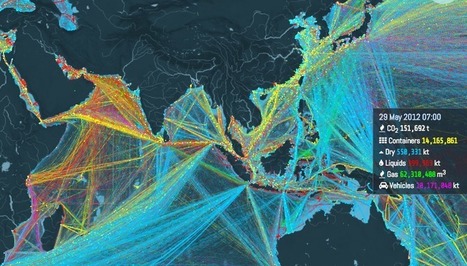
"There are around 6,000 cargo vessels out on the ocean right now, carrying 20,000,000 shipping containers, which are delivering most of the products you see around you. And among all the containers are a special subset of temperature-controlled units known in the global cargo industry, in all seriousness, as reefers. 70% of what we eat passes through the global cold chain, a series of artificially-cooled spaces, which is where the reefer comes into play."
Via Michael Miller
"It is estimated that 97 per cent of all trade – the things we buy in shops – will have been transported in containers by ships at sea. The container vessel, stacked high with uniformly-sized metal boxes, has become a symbol of our globalized world. This is a world of imports and exports, a world where moving things across huge distances keeps the price of daily commodities low as items are manufactured in one place, then packaged in another, before arriving on the shores where they will eventually be sold. In recent geographical literature, attention has turned to the world at sea – a space traditionally overlooked. Geography means ‘Earth-writing’ and geographers have taken the origins of the term very seriously. They have written primarily about the Earth: the ground, the soil, the land. The sea is something ‘out there’ – seemingly disconnected from our everyday lives. However, an appreciation of the world as made from flows and connections has enabled geography to recognize that the sea is essential to our landed life." http://wp.me/p2Ij6x-5DS Tags: transportation, globalization, diffusion, industry, economic.
A new study illustrates just how drastically employment has plunged in Rhode Island’s historic industrial base over recent decades. Since 1980, the Providence metropolitan area has experienced the largest shift in the country away from manufacturing jobs and into work requiring college degrees, according to a paper by Stephan Whitaker, a research economist at the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland. “In 1980, 40% of workers in the Providence metro area worked in manufacturing and 25% worked in degree-intensive fields,” Whitaker writes. “By 2014, manufacturing had dropped to just 11%, and degree-intensive jobs had risen to 47%.” Tags: urban, industry, manufacturing, labor, economic, Rhode Island.
Via Rebecca Cofield
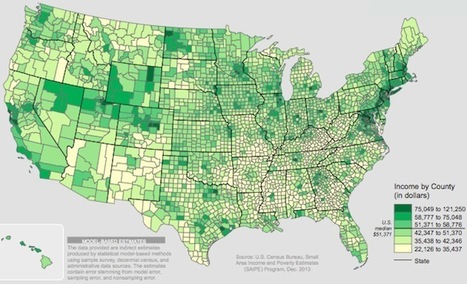
"At the county level, America is a tremendously unequal place."
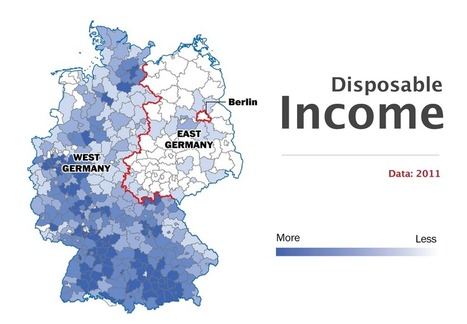
"While 75 percent of Germans who live in the east said that they considered their country's reunification a success, only half of western Germans agreed. With eastern and western Germans blaming each other for past mistakes over the past two years, that frustration has likely increased. Younger citizens, especially — who do not usually identify themselves with their area of origin as strongly anymore — have grown worried about the persistent skepticism on both sides. But where do those divisions come from? And how different are eastern and western Germany today?"
Via CT Blake
"The map above, created with data from Telegeography, shows how those cables have developed since 1990. Most existing cables were constructed during a period of rapid growth in the mid-2000’s. This was followed by a gap of several years during which companies steadily exhausted the available capacity. Over the last few years, explosive new demand, driven by streaming video, has once again jumpstarted the the construction of new cables."
Via GTANSW & ACT
"Ships carry 11 billion tons of goods each year. This interactive map shows where they all go. About 11 billion tons of stuff gets carried around the world every year by large ships. Clothes, flat-screen TVs, grain, cars, oil — transporting these goods from port to port is what makes the global economy go 'round. And now there's a great way to visualize this entire process, through this stunning interactive map from the UCL Energy Institute."
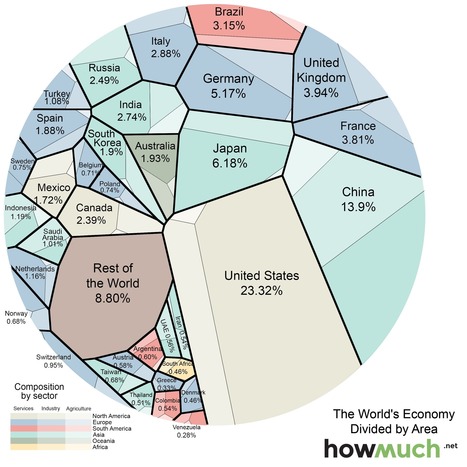
The graphic above (Voronoi diagram) represents the relative size of each country’s economy in terms of nominal GDP: the larger the area, the larger the size of the economy. The areas are further divided into three sectors: services, industrial, and agricultural. The US economy is mostly composed of companies engaged in providing services (79.7% compared to the global average of 63.6%), while agriculture and industry make up smaller-than-average of portions of the economy (1.12% and 19.1% compared to averages of 5.9% and 30.5%). Tags: globalization, industry, economic, visualization.
|
"Once energy dependent, Chile is on track to become a renewables powerhouse with the potential to export electricity. Chile is on track to rely on clean sources for 90 percent of its electricity needs by 2050, up from the current 45 percent."
Via Nancy Watson
"The Seattle-based internet book seller Amazon just announced plans to open an enormous fulfillment center in the North Randall, Ohio. This is a big deal for the small community which has suffered greatly since the Randall Park Mall, once the largest in America, shut down due to retail sales moving online. Amazon is actually building its new warehouse on the same land where the mall once stood. The irony of this is lost on no one."
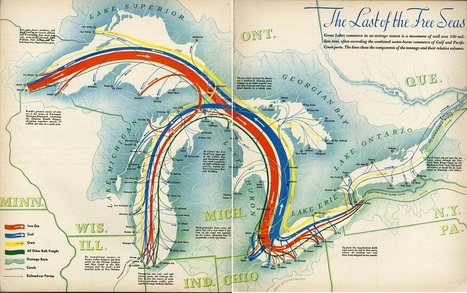
"The Last of the Free Seas is the title of this fantastic map of the Great Lakes made by Boris Artzbasheff. It was published in Fortune Magazine in July 1940."
Via Ben Salve
Amazon’s zero-profit strategy is a disaster for anyone who goes up against it.
The graphic above (Voronoi diagram) represents the relative size of each country’s economy in terms of nominal GDP: the larger the area, the larger the size of the economy. The areas are further divided into three sectors: services, industrial, and agricultural. The US economy is mostly composed of companies engaged in providing services (79.7% compared to the global average of 63.6%), while agriculture and industry make up smaller-than-average of portions of the economy (1.12% and 19.1% compared to averages of 5.9% and 30.5%). Tags: globalization, industry, economic, visualization.
Via Courtney Barrowman
"The ships, railroads, and trucks that transport containers worldwide form the backbone of the global economy. The pace of globalization over the last sixty years has accelerated due to containers; just like canals and railroads defined earlier phases in the development of a global economy. While distance used to be the largest obstacle to regional integration, these successive waves of transportation improvements have functionally made the world a smaller place. Geographers refer to this as the Space-Time Convergence."
Via Michael Miller
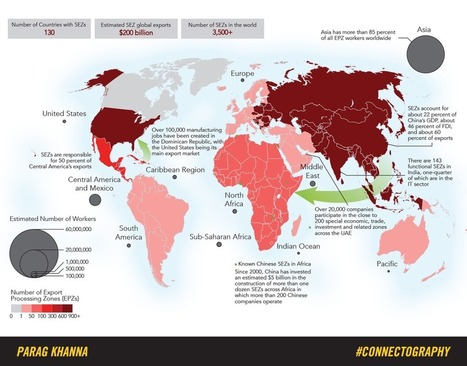
"Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are the most rapidly spreading kind of city, having catapulted exports and growth from Mauritius and the Dominican Republic to Shenzhen and Dubai -- and now across Africa. Today more than 4000 SEZs dot the planet, a major indication of our transition towards the "supply chain world" explored in Connectography. See more maps from Connectography and order the book here." Tags: globalization, urban, economic, industry, regions.
Via Rebecca Cofield
The sugar industry in Hawaii dominated the state's economy for over a century. But it has shrunk in recent years. Now, the last of the state's sugar mills has wrapped up its final harvest.
Via Ben Salve
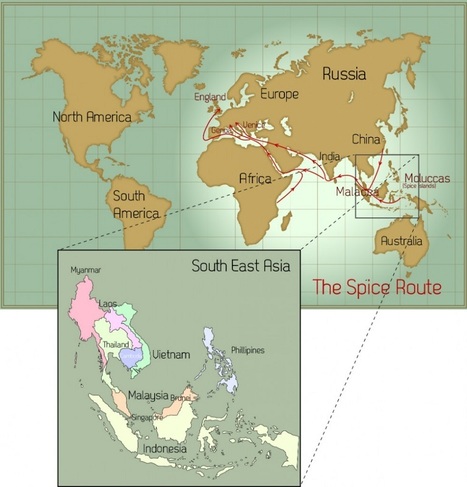
"In its day, the spice trade was the world’s biggest industry. It established and destroyed empires and helped the Europeans (who were looking for alternate routes to the east) map the globe through their discovery of new continents. What was once tightly controlled by the Arabs for centuries was now available throughout Europe with the establishment of the Ocean Spice Trade route connecting Europe directly to South Asia (India) and South East Asia."
Environmental artist J Henry Fair captures the beauty and destruction of industrial sites to illustrate the hidden impacts of the things we buy – the polluted air, destroyed habitats and the invisible carbon heating the planet
"Follow America's favorite vegetable from field to factory — to see how potatoes grow and how they're turned into chips."
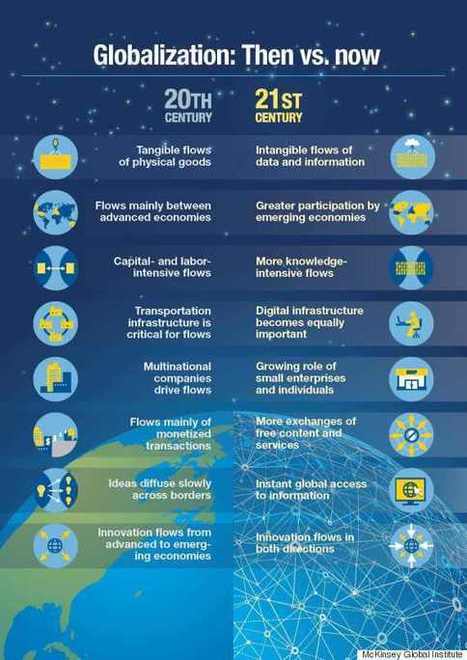
"Yes, globalization. For many people, that word conjures up, at best, images of container ships moving manufactured goods from far-flung factories. At worst, it harkens back to acrid debates about trade deficits, currency wars and jobs moving to China. In fact, since the Great Recession of 2008, the global flow of goods and services has flattened, and cross-border capital flows have declined sharply. But globalization overall isn't on the wane. Like so much in our world today, it has reinvented itself by going digital." Tags: technology, globalization, diffusion, industry, economic.
Via Tony Hall
|



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...