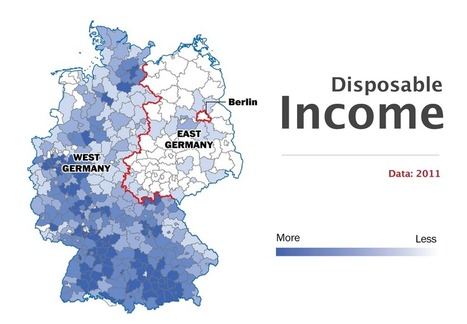
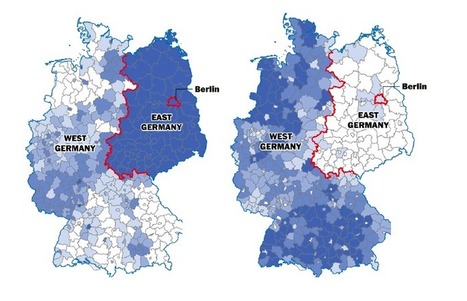
"While 75 percent of Germans who live in the east said that they considered their country's reunification a success, only half of western Germans agreed. With eastern and western Germans blaming each other for past mistakes over the past two years, that frustration has likely increased. Younger citizens, especially — who do not usually identify themselves with their area of origin as strongly anymore — have grown worried about the persistent skepticism on both sides. But where do those divisions come from? And how different are eastern and western Germany today?"
Via CT Blake



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...