Immunotherapies for cancer are demonstrating increasing success. These agents can amplify existent antitumour immunity or induce durable antitumour immune responses in a wide array of cancers. The spectrum of immunotherapeutics is broad, spanning monoclonal antibodies and their derivatives, tumour vaccines, and adoptive therapies using T cells and natural killer cells.
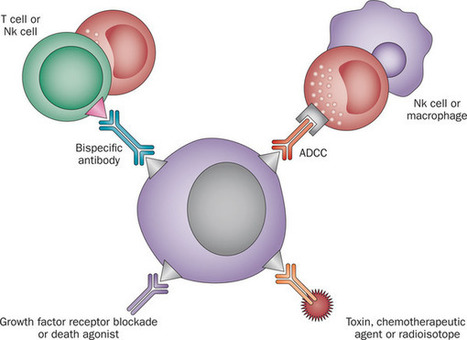
Only a small number of immunotherapies have been tested in paediatric cancers, but impressive antitumour effects have already been observed. Mononclonal antibodies targeting GD2 that induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity improve survival in high-risk neuroblastoma. Bi-specific monoclonal antibodies that simultaneously target CD19 and activate T cells can induce remission in acute B-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL) and adoptive immunotherapy using T cells genetically engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors targeting CD19 induce impressive responses in B-ALL. Efforts are underway to generate and test new immunotherapies in a wider array of paediatric cancers. Major challenges include a need to identify immunotherapy targets on the most lethal childhood cancers, to expand availability of technology-intense platforms, such as adoptive cell therapy, to optimize management of novel toxicities associated with this new class of cancer therapies and to determine how best to incorporate these therapies into standard treatment paradigms.
Via
Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...









Int. Immunol. (2015) 27 (1): 31-37 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxu089
Correspondence to: Z. Zimmerman, One Amgen Center Drive, MS 38-B-A, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320, USA; E-mail: zacharyz@amgen.com