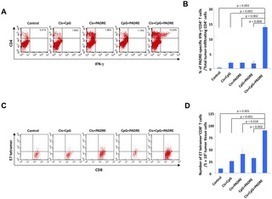
Chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy are widely used as cancer treatments, but the antitumor effects they produce can be enhanced when combined with immunotherapies. Chemotherapy kills tumor cells, but it also releases tumor antigen and allows the cross-presentation of the tumor antigen to trigger antigen-specific cell-mediated immune responses. Promoting CD4+ T helper cell immune responses can be used to enhance the cross-presentation of the tumor antigen following chemotherapy. The pan HLA-DR binding epitope (PADRE peptide) is capable of generating antigen-specific CD4+ T cells that bind various MHC class II molecules with high affinity and has been widely used in conjunction with vaccines to improve their potency by enhancing CD4+ T cell responses. Here, we investigated whether intratumoral injection of PADRE and the adjuvant CpG into HPV16 E7-expressing TC-1 tumors following cisplatin chemotherapy could lead to potent antitumor effects and antigen-specific cell-mediated immune responses. We observed that treatment with all three agents produced the most potent antitumor effects compared to pairwise combinations. Moreover, treatment with cisplatin, CpG and PADRE was able to control tumors at a distant site, indicating that our approach is able to induce cross-presentation of the tumor antigen. Treatment with cisplatin, CpG and PADRE also enhanced the generation of PADRE-specific CD4+ T cells and E7-specific CD8+ T cells and decreased the number of MDSCs in tumor loci. The treatment regimen presented here represents a universal approach to cancer control.
Via Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...








Citation: Song L, Yang M-C, Knoff J, Wu T-C, Hung C-F (2014) Cancer Immunotherapy Employing an Innovative Strategy to Enhance CD4+ T Cell Help in the Tumor Microenvironment. PLoS ONE 9(12): e115711. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115711