AbstractEnhancing immune responses with immune-modulatory monoclonal antibodies directed to inhibitory immune receptors is a promising modality in cancer therapy. Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated with antibodies blocking inhibitory immune checkpoints such as cytotoxic T lymphocyte–associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) or PD-1/PD-L1. Treatment with ipilimumab, a fully human CTLA-4–specific mAb, showed durable clinical efficacy in metastatic melanoma; its mechanism of action is, however, only partially understood. This is a study of 29 patients with advanced cutaneous melanoma treated with ipilimumab. We analyzed peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and matched melanoma metastases from 15 patients responding and 14 not responding to ipilimumab by multicolor flow cytometry, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) assay, and immunohistochemistry. PBMCs and matched tumor biopsies were collected 24 h before (i.e., baseline) and up to 4 wk after ipilimumab. Our findings show, to our knowledge for the first time, that ipilimumab can engage ex vivo FcγRIIIA (CD16)-expressing, nonclassical monocytes resulting in ADCC-mediated lysis of regulatory T cells (Tregs). In contrast, classical CD14++CD16−monocytes are unable to do so. Moreover, we show that patients responding to ipilimumab display significantly higher baseline peripheral frequencies of nonclassical monocytes compared with nonresponder patients. In the tumor microenvironment, responders have higher CD68+/CD163+ macrophage ratios at baseline and show decreased Treg infiltration after treatment. Together, our results suggest that anti–CTLA-4 therapy may target Tregs in vivo. Larger translational studies are, however, warranted to substantiate this mechanism of action of ipilimumab in patients.
Via Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...








PNAS
Emanuela Romano, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417320112
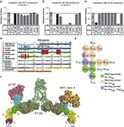
Ipilimumab-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of regulatory T cells ex vivo by nonclassical monocytes in melanoma patientsEmanuela Romanoa,b,c,1, Monika Kusio-Kobialkab, Periklis G. Foukasc,d, Petra Baumgaertnerc,Christiane Meyerc, Pierluigi Ballabenie, Olivier Michielina,c, Benjamin Weidef, Pedro Romeroc, andDaniel E. SpeisercAuthor Affiliations
Edited by Ira Mellman, Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA, and approved March 30, 2015 (received for review September 9, 2014)
PNAS
Emanuela Romano, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417320112
Ipilimumab-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of regulatory T cells ex vivo by nonclassical monocytes in melanoma patientsEmanuela Romanoa,b,c,1, Monika Kusio-Kobialkab, Periklis G. Foukasc,d, Petra Baumgaertnerc,Christiane Meyerc, Pierluigi Ballabenie, Olivier Michielina,c, Benjamin Weidef, Pedro Romeroc, andDaniel E. Speiserc
Author Affiliations
Edited by Ira Mellman, Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA, and approved March 30, 2015 (received for review September 9, 2014)