Abstract
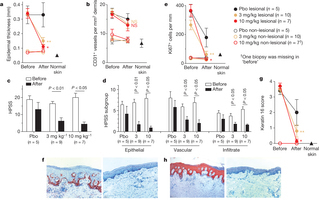
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that affects approximately 2–3% of the population worldwide and has severe effects on patients’ physical and psychological well-being1, 2, 3. The discovery that psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease has led to more targeted, effective therapies; recent advances have focused on the interleukin (IL)-12/23p40 subunit shared by IL-12 and IL-23. Evidence suggests that specific inhibition of IL-23 would result in improvement in psoriasis. Here we evaluate tildrakizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-23p19 subunit, in a three-part, randomized, placebo-controlled, sequential, rising multiple-dose phase I study in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis to provide clinical proof that specific targeting of IL-23p19 results in symptomatic improvement of disease severity in human subjects. A 75% reduction in the psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score (PASI75) was achieved by all subjects in parts 1 and 3 (pooled) in the 3 and 10 mg kg−1 groups by day 196. In part 2, 10 out of 15 subjects in the 3 mg kg−1 group and 13 out of 14 subjects in the 10 mg kg−1 group achieved a PASI75 by day 112. Tildrakizumab demonstrated important clinical improvement in moderate-to-severe psoriasis patients as demonstrated by improvements in PASI scores and histological samples.
Via Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...








NATURE | LETTER
Clinical improvement in psoriasis with specific targeting of interleukin-23Tamara Kopp,Elisabeth Riedl,Christine Bangert,Edward P. Bowman,Elli Greisenegger,Ann Horowitz,Harald Kittler,Wendy M. Blumenschein,Terrill K. McClanahan,Thomas Marbury,Claus Zachariae,Danlin Xu,Xiaoli Shirley Hou,Anish Mehta,Anthe S. Zandvliet,Diana Montgomery,Frank van Aarle& Sauzanne KhaliliehAffiliationsContributionsCorresponding authorNature 521, 222–226 (14 May 2015) doi:10.1038/nature14175Received 23 December 2013 Accepted 23 December 2014 Published online 09 March 2015Corrected online 13 May 2015