Large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive capabilities in generating
realistic text across diverse subjects. Concerns have been raised that they
could be utilized to produce fake content with a deceptive intention, although
evidence thus far remains anecdotal. This paper presents a case study about a
Twitter botnet that appears to employ ChatGPT to generate human-like content.
Through heuristics, we identify 1,140 accounts and validate them via manual
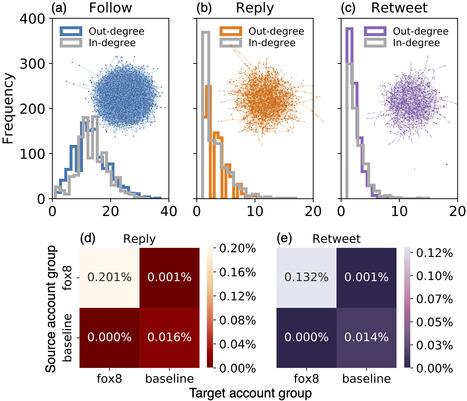
annotation. These accounts form a dense cluster of fake personas that exhibit
similar behaviors, including posting machine-generated content and stolen
images, and engage with each other through replies and retweets.
ChatGPT-generated content promotes suspicious websites and spreads harmful
comments. While the accounts in the AI botnet can be detected through their
coordination patterns, current state-of-the-art LLM content classifiers fail to
discriminate between them and human accounts in the wild. These findings
highlight the threats posed by AI-enabled social bots.
Read the full article at: arxiv.org



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...