Authors: Yaron Caspi, Chrysoula K. Pantazopoulou, Jeanine J. Prompers, Corné MJ Pieterse, Hilleke Hulshoff Pol and Kaisa Kajala.
eLife (2023)
Editor's view: Recent findings about the possible intercellular signalling role of glutamate, GABA, and melatonin might help to establish hypotheses concerning the evolutionary factors that caused intercellular organisms to use specific molecules in intercellular signalling.
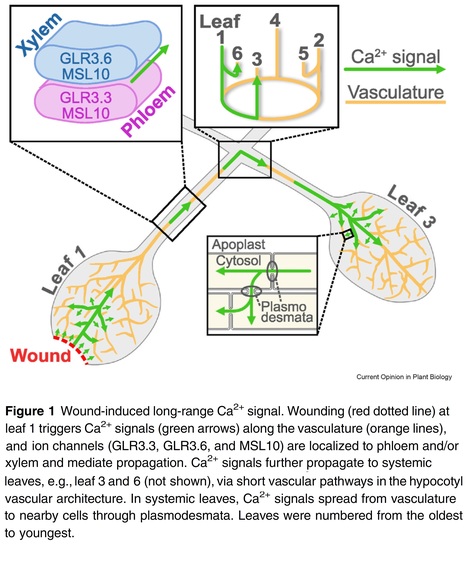
Abstract: "Intercellular signalling is an indispensable part of multicellular life. Understanding the commonalities and differences in how signalling molecules function in two remote branches of the tree of life may shed light on the reasons these molecules were originally recruited for intercellular signalling. Here we review the plant function of three highly studied animal intercellular signalling molecules, namely glutamate, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and melatonin. By considering both their signalling function in plants and their broader physiological function, we suggest that molecules with an original function as key metabolites or active participants in reactive ion species scavenging have a high chance of becoming intercellular signalling molecules. Naturally, the evolution of machinery to transduce a message across the plasma membrane is necessary. This fact is demonstrated by three other well-studied animal intercellular signalling molecules, namely serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine, for which there is currently no evidence that they act as intercellular signalling molecules in plants."


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...