|
Scooped by Julio Retamales |
Authors: Yu Gu, Jie Zhang, Le Liu, Ghulam Qanmber, Zhao Liu, Kun Xing, Lili Lu, Li Liu, Shuya Ma, Fuguang Li and Zuoren Yang.
The Plant Journal (2023)
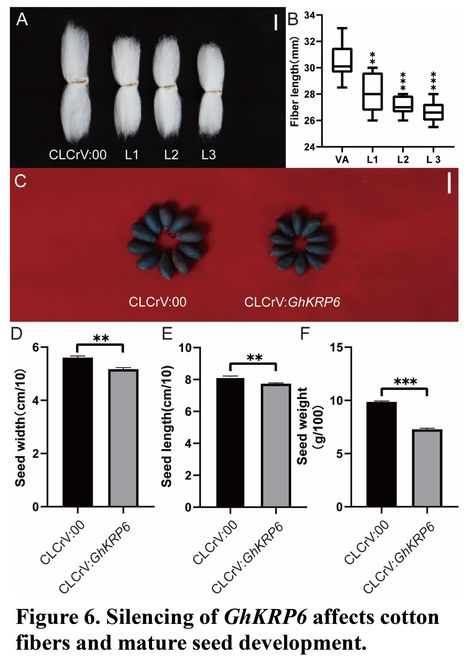
Abstract: "The steroidal hormone brassinosteroid (BR) has been shown to positively regulate cell expansion in plants. However, the specific mechanism by which BR controls this process has not been fully understood. In this study, RNA-seq and DAP-seq analysis of GhBES1.4 (a core transcription factor in BR signaling) were used to identify a cotton cell cycle-dependent kinase inhibitor called GhKRP6. The study found that GhKRP6 was significantly induced by the BR hormone, and that GhBES1.4 directly promoted the expression of GhKRP6 by binding to the CACGTG motif in its promoter region. GhKRP6-silenced cotton plants had smaller leaves with more cells and reduced cell size. Furthermore, endoreduplication was inhibited, which affected cell expansion and ultimately decreased fiber length and seed size in GhKRP6-silenced plants compared with the control. The KEGG enrichment results of control and VIGS-GhKRP6 plants revealed differential expression of genes related to cell wall biosynthesis, MAPK, and plant hormone transduction pathways – all of which are related to cell expansion. Additionally, some cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) genes were up-regulated in the plants with silenced GhKRP6. Our study also found that GhKRP6 could interact directly with a cell cycle-dependent kinase called GhCDKG. Taken together, these results suggest that BR signaling influences cell expansion by directly modulating the expression of cell cycle-dependent kinase inhibitor GhKRP6 via GhBES1.4."
No comment yet.
Sign up to comment


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...