Authors: Keisuke Nagai and Motoyuki Ashikari
Breeding Science (2023)
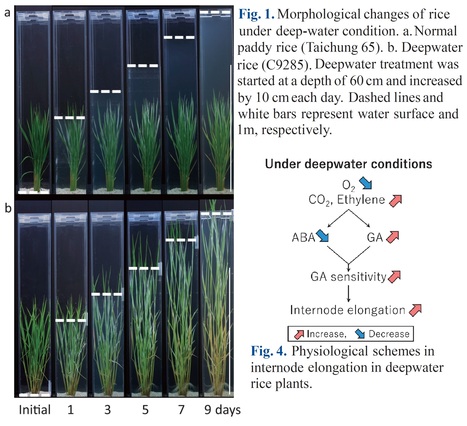
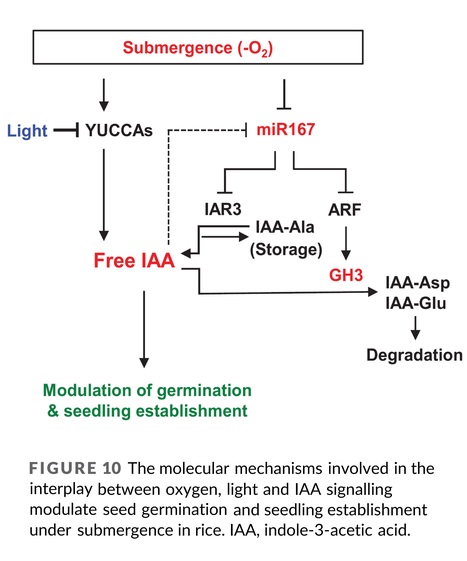
Abstract: "Rice plants that form ventilated tissues, such as aerenchyma in the leaves, stems, and roots, allow for growth in waterlogged conditions (paddy fields), but they cannot breathe and drown in flooded environments where the whole plant body is submerged. However, deepwater rice plants grown in flood-prone areas of Southeast Asia survive in prolonged flooded environments by taking in air through an elongated stem (internode) and leaves that emerge above the water surface, even if the water level is several meters high and flooding continues for several months. Although it has been known that plant hormones, such as ethylene and gibberellins, promote internode elongation in deepwater rice plants, the genes that control rapid internode elongation during submergence have not been identified. We recently identified several genes responsible for the quantitative trait loci involved in internode elongation in deepwater rice. Identification of the genes revealed a molecular gene network from ethylene to gibberellins in which internode elongation is promoted by novel ethylene-responsive factors and enhances gibberellin responsiveness at the internode. In addition, elucidation of the molecular mechanism of internode elongation in deepwater rice will help our understanding of the internode elongation mechanism in normal paddy rice and contribute to improving crops through the regulation of internode elongation."


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...