Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Authors: David Jiménez-Arias, Sarai Morales-Sierra, Emma Suárez, Jorge Lozano-Juste, Alberto Coego, Juan C. Estevez, Andrés A. Borges and Pedro L. Rodriguez.
Frontiers in Plant Science (2023)
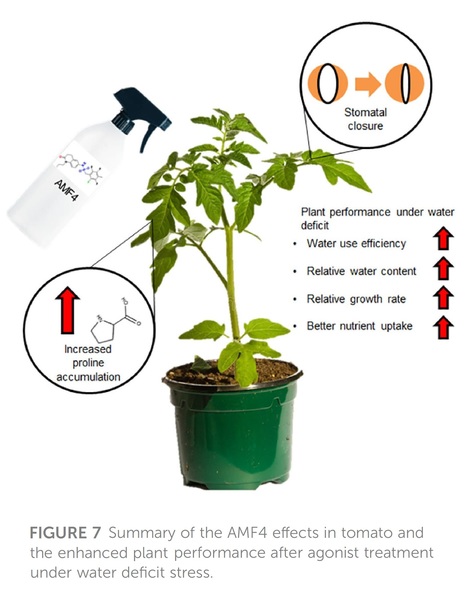
Abstract: "Water deficit represents a serious limitation for agriculture and both genetic and chemical approaches are being used to cope with this stress and maintain plant yield. Next-generation agrochemicals that control stomatal aperture are promising for controlling water use efficiency. For example, chemical control of abscisic acid (ABA) signaling through ABA-receptor agonists is a powerful method to activate plant adaptation to water deficit. Such agonists are molecules able to bind and activate ABA receptors and, although their development has experienced significant advances in the last decade, few translational studies have been performed in crops. Here, we describe protection by the ABA mimic-fluorine derivative 4 (AMF4) agonist of the vegetative growth in tomato plants subjected to water restriction. Photosynthesis in mock-treated plants is markedly impaired under water deficit conditions, whereas AMF4 treatment notably improves CO2 assimilation, the relative plant water content and growth. As expected for an antitranspirant molecule, AMF4 treatment diminishes stomatal conductance and transpiration in the first phase of the experiment; however, when photosynthesis declines in mock-treated plants as stress persists, higher photosynthetic and transpiration parameters are recorded in agonist-treated plants. Additionally, AMF4 increases proline levels over those achieved in mock-treated plants in response to water deficit. Thus water deficit and AMF4 cooperate to upregulate P5CS1 through both ABA-independent and ABA-dependent pathways, and therefore, higher proline levels are produced Finally, analysis of macronutrients reveals higher levels of Ca, K and Mg in AMF4- compared to mock-treated plants subjected to water deficit. Overall, these physiological analyses reveal a protective effect of AMF4 over photosynthesis under water deficit and enhanced water use efficiency after agonist treatment. In summary, AMF4 treatment is a promising approach for farmers to protect the vegetative growth of tomatoes under water deficit stress.
Authors: Daisuke Takagi, Keiki Ishiyama, Mao Suganami, Tomokazu Ushijima, Takeshi Fujii, Youshi Tazoe, Michio Kawasaki, Ko Noguchi and Amane Makino.
Scientific Reports (2021)
Abstract: "Despite the essentiality of Mn in terrestrial plants, its excessive accumulation in plant tissues can cause growth defects, known as Mn toxicity. Mn toxicity can be classified into apoplastic and symplastic types depending on its onset. Symplastic Mn toxicity is hypothesised to be more critical for growth defects. However, details of the relationship between growth defects and symplastic Mn toxicity remain elusive. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying symplastic Mn toxicity in rice plants. We found that under excess Mn conditions, CO2 assimilation was inhibited by stomatal closure, and both carbon anabolic and catabolic activities were decreased. In addition to stomatal dysfunction, stomatal and leaf anatomical development were also altered by excess Mn accumulation. Furthermore, indole acetic acid (IAA) concentration was decreased, and auxin-responsive gene expression analyses showed IAA-deficient symptoms in leaves due to excess Mn accumulation. These results suggest that excessive Mn accumulation causes IAA deficiency, and low IAA concentrations suppress plant growth by suppressing stomatal opening and leaf anatomical development for efficient CO2 assimilation in leaves."
|
Authors: Xi Chen, Steven M. Smith, Sergey Shabala and Min Yu.
Journal of Experimental Botany (2023)
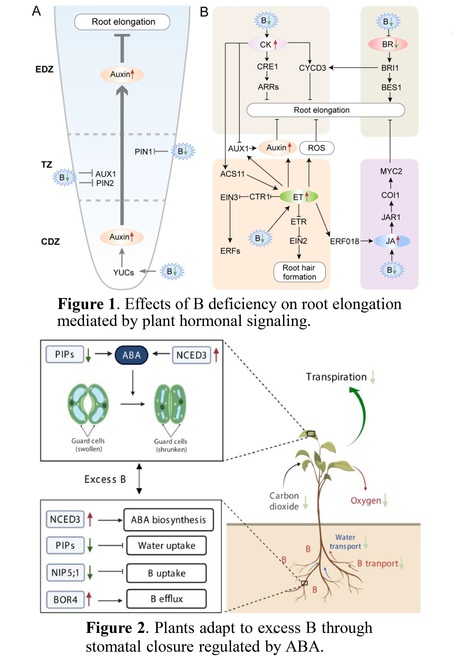
Abstract: "Boron (B) is an essential element for plant growth. Many agricultural soils around the globe have either insufficient or excessive amounts of available B, with major implications for crop production. Understanding major limitations imposed by B nutritional disorders may allow breeding crops for improved B use efficiency as well as make them more resilient to excessive B, thus reducing yield penalties. It has become apparent that B-related physiological disorders are mediated in large part by their impact on plant hormonal production and signaling. The aim of this review is to summarize the current knowledge of the roles of hormones in plant responses to B and their impact on plant growth and development. The most significant effect of B deficiency is the inhibition of root elongation. B deficiency promotes the redistribution of auxin in the root elongation zone. Together with cytokinin signals and ethylene, this redistribution and modulation of auxin content triggers inhibition of the root cell elongation. Under B deficiency, root development is also regulated by brassinosteroids and jasmonic acid. Excess B can induce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Abscisic acid and salicylic acid are both produced in response to B toxicity, and both can induce the antioxidant defense system to detoxify ROS. Another adaptation to B toxicity involves changes in the expression levels and activity of aquaporins in roots, thus reducing the uptake of water and delivery of B into the transpiration stream. In addition, abscisic acid mediates stomatal closure to further limit transpiration and the consequent accumulation of B in leaves."
Authors: Daisuke Takagi, Keiki Ishiyama, Mao Suganami, Tomokazu Ushijima, Takeshi Fujii, Youshi Tazoe, Michio Kawasaki, Ko Noguchi and Amane Makino.
bioRxiv (2021)
Abstract: "Despite the essentiality of Mn in terrestrial plants, its excessive accumulation in plant tissues causes growth defects, known as Mn toxicity. Mn toxicity can be divided into apoplastic and symplastic types depending on its onset. For growth defects, symplastic rather than apoplastic Mn toxicity is hypothesised to be more critical. However, details of the relationship between growth defects and symplastic Mn toxicity remains elusive. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of symplastic Mn toxicity in rice plants. We found that under excess Mn conditions, CO2 assimilation was inhibited by stomatal closure, and both carbon anabolic and catabolic activities were decreased. In addition to stomatal dysfunction, stomatal and leaf anatomical development were also altered by excess Mn accumulation. Furthermore, the indole acetic acid (IAA) concentration was decreased, and auxin-responsive gene expression analyses showed IAA-deficient symptoms in leaves due to excess Mn accumulation. These results suggest that excessive Mn accumulation causes IAA deficiency, and low IAA concentrations suppress plant growth by suppressing stomatal opening and leaf anatomical development for efficient CO2 assimilation in leaves."
|


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...