Since December, 2019, Wuhan, China, has experienced an outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of patients with COVID-19 have been reported but risk factors for mortality and a detailed clinical course of illness, including viral shedding, have not been well described.
In this retrospective, multicentre cohort study, we included all adult inpatients (≥18 years old) with laboratory- confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital (Wuhan, China) who had been discharged or had died by Jan 31, 2020. Demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data, including serial samples for viral RNA detection, were extracted from electronic medical records and compared between survivors and non-survivors. We used univariable and multivariable logistic regression methods to explore the risk factors associated with in-hospital death.
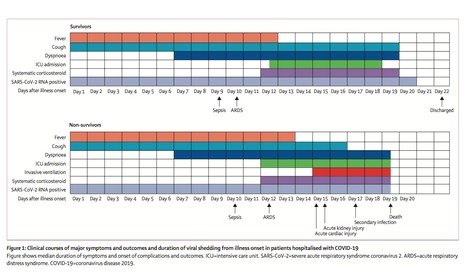
191 patients (135 from Jinyintan Hospital and 56 from Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital) were included in this study, of whom 137 were discharged and 54 died in hospital. 91 (48%) patients had a comorbidity, with hypertension being the most common (58 [30%] patients), followed by diabetes (36 [19%] patients) and coronary heart disease (15 [8%] patients). Multivariable regression showed increasing odds of in-hospital death associated with older age (odds ratio 1·10, 95% CI 1·03–1·17, per year increase; p=0·0043), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5·65, 2·61–12·23; p<0·0001), and d-dimer greater than 1 μg/L (18·42, 2·64–128·55; p=0·0033) on admission. Median duration of viral shedding was 20·0 days (IQR 17·0–24·0) in survivors, but SARS-CoV-2 was detectable until death in non-survivors. The longest observed duration of viral shedding in survivors was 37 days.
The criteria for discharge were absence of fever for at least 3 days, substantial improvement in both lungs in chest CT, clinical remission of respiratory symptoms, and two throat-swab samples negative for SARS-CoV-2 RNA obtained at least 24 h apart...
For survivors, the median duration of viral shedding was 20·0 days (IQR 17·0–24·0) from illness onset, but the virus was continuously detectable until death in non- survivors (table 2; figure 1). The shortest observed duration of viral shedding among survivors was 8 days, whereas the longest was 37 days.
Published March 9, 2020 in The Lancet:
https://doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(20)30566-3



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...