Highlights
- RNA expression of retroviral element RNLTR12-int is crucial for myelination
- RNLTR12-int binds to SOX10 to regulate Mbp expression
- RNLTR12-int-like sequences (RetroMyelin) were identified in all jawed vertebrates
- Convergent evolution likely led to RetroMyelin acquisition, adapted for myelination
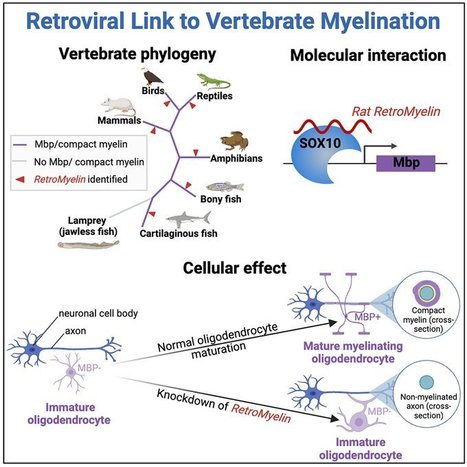
Summary
Myelin, the insulating sheath that surrounds neuronal axons, is produced by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS). This evolutionary innovation, which first appears in jawed vertebrates, enabled rapid transmission of nerve impulses, more complex brains, and greater morphological diversity. Here, we report that RNA-level expression of RNLTR12-int, a retrotransposon of retroviral origin, is essential for myelination. We show that RNLTR12-int-encoded RNA binds to the transcription factor SOX10 to regulate transcription of myelin basic protein (Mbp, the major constituent of myelin) in rodents. RNLTR12-int-like sequences (which we name RetroMyelin) are found in all jawed vertebrates, and we further demonstrate their function in regulating myelination in two different vertebrate classes (zebrafish and frogs). Our study therefore suggests that retroviral endogenization played a prominent role in the emergence of vertebrate myelin.
Published in Cell (Feb. 15, 2024):



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...