Highlights
- C19MC Alu RNA, and not the miRNAs, induces constitutive IFNL and antiviral protection
- C19MC produces high levels of Alu dsRNA and induces IFNL through RLRs and PKR
- C2MCΔ/Δ mouse placentas display low IFN and increased viral vertical transmission
- Alu and B1 SINEs are an integral part of the antiviral innate immune response
Summary
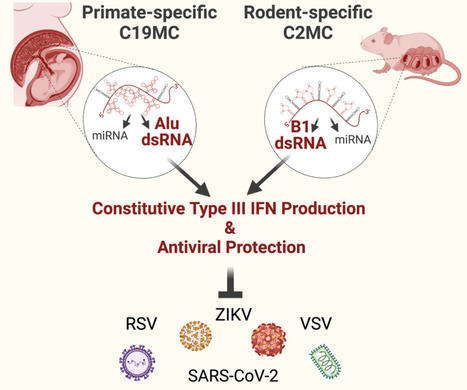
Hemochorial placentas have evolved defense mechanisms to prevent the vertical transmission of viruses to the immunologically underdeveloped fetus. Unlike somatic cells that require pathogen-associated molecular patterns to stimulate interferon production, placental trophoblasts constitutively produce type III interferons (IFNL) through an unknown mechanism. We demonstrate that transcripts of short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) embedded in miRNA clusters within the placenta trigger a viral mimicry response that induces IFNL and confers antiviral protection.
Alu SINEs within primate-specific chromosome 19 (C19MC) and B1 SINEs within rodent-specific microRNA cluster on chromosome 2 (C2MC) produce dsRNAs that activate RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) and downstream IFNL production. Homozygous C2MC knockout mouse trophoblast stem (mTS) cells and placentas lose intrinsic IFN expression and antiviral protection, whereas B1 RNA overexpression restores C2MCΔ/Δ mTS cell viral resistance. Our results uncover a convergently evolved mechanism whereby SINE RNAs drive antiviral resistance in hemochorial placentas, placing SINEs as integral players in innate immunity.
Published in Cell Host and Microbe (July 12, 2023):



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...