|
Scooped by Juan Lama |
Continued SARS-CoV-2 infection among immunocompromised individuals is likely to play a role in generating genomic diversity and the emergence of novel variants. Antiviral treatments such as molnupiravir are used to mitigate severe COVID-19 outcomes, but the extended effects of these drugs on viral evolution in patients with chronic infections remain uncertain. This study investigates how molnupiravir affects SARS-CoV-2 evolution in immunocompromised patients with prolonged infections.
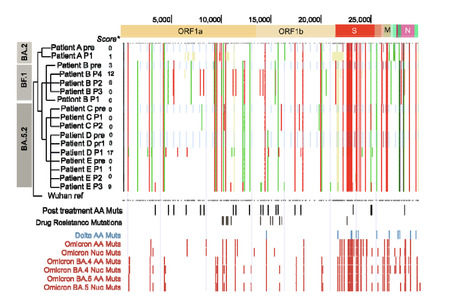
The study included five immunocompromised patients treated with molnupiravir and four patients not treated with molnupiravir (two immunocompromised and two non-immunocompromised). We selected patients who had been infected by similar SARS-CoV-2 variants and with high-quality genomes across timepoints to allow comparison between groups. Throat and nasopharyngeal samples were collected in patients up to 44 days post treatment and were sequenced using tiled amplicon sequencing followed by variant calling. The UShER pipeline and University of California Santa Cruz genome viewer provided insights into the global context of variants. Treated and untreated patients were compared, and mutation profiles were visualised to understand the impact of molnupiravir on viral evolution.
Patients treated with molnupiravir showed a large increase in low-to-mid-frequency variants in as little as 10 days after treatment, whereas no such change was observed in untreated patients. Some of these variants became fixed in the viral population, including non-synonymous mutations in the spike protein. The variants were distributed across the genome and included unique mutations not commonly found in global omicron genomes. Notably, G-to-A and C-to-T mutations dominated the mutational profile of treated patients, persisting up to 44 days post treatment.
Molnupiravir treatment in immunocompromised patients led to the accumulation of a distinctive pattern of mutations beyond the recommended 5 days of treatment. Treated patients maintained persistent PCR positivity for the duration of monitoring, indicating clear potential for transmission and subsequent emergence of novel variants.
Published in The Lancet Microbe (March 22, 2024):
No comment yet.
Sign up to comment



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...