The bioengineered immune players called CAR T cells last longer and work better if pumped up with a large dose of a protein that makes them resemble stem cells.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account

| Tags |
|---|
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
Since its breakthrough development more than a decade ago, CRISPR has revolutionized DNA editing across a broad range of fields.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Researchers have developed a new genetic system to test and analyze the mechanisms underlying the results of CRISPR-based DNA repair. As described in Nature Communications, they have developed a sequence analyzer to help track on- and off-target mutational changes and how they are inherited from one generation to the next. The tool, called Integrated Classifier Pipeline (ICP), can reveal specific categories of mutations resulting from CRISPR editing. Developed in flies and mosquitoes, ICP provides a "fingerprint" of how genetic material is inherited, enabling scientists to track the source of mutational changes and the associated risks emerging from potentially problematic modifications. PKI can help unravel the complex biological issues that arise when determining the mechanisms behind CRISPR. Although developed in insects, ICP has great potential for human applications.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and lumbar puncture (LP) may not always be necessary for diagnosing and managing a serious neurological complication associated with CAR T-cell therapy, according to a new Blood Advances study.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
A study published in Blood Advances reveals that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and lumbar puncture (LP) may not be systematically necessary in the diagnosis and management of severe cases of neurotoxicity linked to CAR T cell therapy. Instead, electroencephalogram (EEG), a non-invasive test, has proved useful in the management of these complications. The researchers examined the usefulness of these tests in 190 patients treated with CAR-T at Rennes University Hospital, where during treatment around 48% of patients developed immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). The researchers assessed how the different tests affected patient treatment, such as how medications, e.g. antibiotics and anti-epileptic treatments, were prescribed based on abnormal results, and how these treatments altered patient outcomes. The results ultimately revealed that abnormal findings were more common in patients with more severe ICANS. MRI findings were often normal, and although LP and EEG often showed abnormalities, they were more common in more severe cases of ICANS. When it came to therapeutic decisions, MRI rarely led to changes, LP sometimes led to unnecessary treatments in cases of suspected infections, and EEG often resulted in adjustments to antiepileptic drugs.
In vivo CRISPR genome-wide screening pinpoints the transcriptional modulator CITED2 as a pivotal driver in the progression of prostate cancer to bone metastasis.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
In vivo screening of the CRISPR genome identifies the transcriptional modulator CITED2 as an essential factor in the progression of prostate cancer to bone metastases. The discovery not only improves understanding of the molecular basis of the disease, but also opens up new avenues for targeted therapies, potentially revolutionizing treatment paradigms for patients battling advanced prostate cancer. The study meticulously engineered non-metastatic human prostate cancer cell lines to activate or inhibit gene expression using CRISPRa or CRISPRi technology. Modified cancer cells were then implanted into the prostate of nude mice, and following tumor development and emergence of metastases, primary and metastatic tumors were harvested for analysis. In vivo CRISPR screening identified CITED2 as an important promoter of bone metastasis, standing out among various genes for its substantial impact. Subsequent functional validation experiments, including innovative organ-on-a-chip assays, reinforced CITED2's role in promoting bone invasion, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. The research also looked at CITED2-driven transcriptional profiles, revealing distinct patterns of primary and metastatic cancer, which could inform the development of precision medicine approaches.
Over the past two decades, the immune system has attracted increasing attention for its role in fighting cancer.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
CRISPR-based gene editing has become a mainstay of biological discovery, providing relatively rapid insight into the function of individual genes and targets for new therapies. However, the main challenge is that it is difficult to edit immune cells without changing their biology, hampering the ability to study immune cell behavior in all its complexity in a living organism. In an earlier study, researchers used CHimeric IMmune Editing (CHIME) to knock out a gene called Ptpn2, which has shown promise for cancer immunotherapy. The recent study published in Nature Immunology explores methods to increase the precision and versatility of CHIME, including simultaneous deletion of multiple genes and targeted application in specific cell types, also using CRISPR to disrupt genes in the edited cells once they were already back inside the animal. This research has successfully demonstrated the feasibility of various innovative approaches to genetic manipulation, offering new avenues for the study of immune gene function.
From
www
Current approaches for inserting autonomous transgenes into the genome, such as CRISPR–Cas9 or virus-based strategies, have limitations including low efficiency and high risk of untargeted genome mutagenesis. Here, we describe precise RNA-mediated insertion of transgenes (PRINT), an approach for site-specifically primed reverse transcription that directs transgene synthesis directly into the genome at a multicopy safe-harbor locus. PRINT uses delivery of two in vitro transcribed RNAs: messenger RNA encoding avian R2 retroelement-protein and template RNA encoding a transgene of length validated up to 4 kb. The R2 protein coordinately recognizes the target site, nicks one strand at a precise location and primes complementary DNA synthesis for stable transgene insertion. With a cultured human primary cell line, over 50% of cells can gain several 2 kb transgenes, of which more than 50% are full-length. PRINT advantages include no extragenomic DNA, limiting risk of deleterious mutagenesis and innate immune responses, and the relatively low cost, rapid production and scalability of RNA-only delivery. Transgenes are inserted into human cells by 2-RNA delivery of a retroelement protein and template.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
The recent approval of a CRISPR-Cas9 therapy for sickle-cell anemia demonstrates that gene-editing tools can do an excellent job of eliminating genes to cure inherited diseases. But it is still not possible to insert entire genes into the human genome to replace them with defective or deleterious genes. A new technique, called RNA-mediated Precise Transgene Insertion, or PRINT, exploits the ability of certain retrotransposons to efficiently insert whole genes into the genome without affecting other genome functions. PRINT would complement the recognized ability of CRISPR-Cas technology to deactivate genes, perform point mutations and insert short segments of DNA. For PRINT, one piece of delivered RNA encodes a common retroelement protein called the R2 protein, which has several active parts, including a nickase and a reverse transcriptase. The other RNA is the template for the transgenic DNA to be inserted, as well as the elements controlling gene expression
study evaluates senolytic CAR T-cell therapy targeting uPAR-positive cells in aged mice, showing its effectiveness in mitigating age-related metabolic dysfunction and offering a potential long-lasting treatment for aging-associated conditions.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Cellular senescence is an irreversible cell cycle arrest induced in response to stress. Under stressful conditions, matrix remodeling enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines are produced, termed Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP). In young individuals with physiological conditions, such as tumor suppression and wound healing, SASP facilitates the recruitment of immune cells, which facilitate tissue restoration and the elimination of senescent cells. In the elderly, senescent cells accumulate due to reduced immune system function and increased tissue damage. To date, most senescent therapies include small-molecule drugs that require repeated administration and poorly target the affected area. A recent study in Nature Aging evaluates the efficacy of a senolytic therapy based on CAR-T cells. This therapy targets urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR)-positive cells, which accumulate during aging. In this study, senolytic cell therapies were shown to alleviate symptoms associated with physiological aging, including metabolic dysfunction.
A new light-inducible RNA base editing tool, padCas13, combines the specificity of CRISPR-Cas13 with the control of light activation and allows for precise, reversible RNA targeting and degradation in mammalian cells, both in vitro and in vivo.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
The padCas13 editor can efficiently edit A-to-I and C-to-U RNA bases, targeting disease-relevant transcripts. Photoactivatable base editing represents a significant advance in CRISPR technology, as it enables fine-tuning of gene expression and post-translational modifications without permanent alterations to the genome. This method is particularly relevant for diseases in which transient modulation of gene expression may have therapeutic benefits. A crucial element of padCas13 is the Magnet system, which comprises a positively and negatively charged Magnet protein. These proteins are designed to heterodimerize rapidly in response to light, thereby activating the Cas13 nuclease.
Using CRISPR, an immune system bacteria use to protect themselves from viruses, scientists have harnessed the power to edit genetic information within cells.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Researchers set out to develop a robust off-switch for the highly efficient Cas3 system they had previously discovered from Neisseria lactima, a bacterium that lives harmlessly in the human upper respiratory tract. Examining all known anti-CRISPRs that have been reported in the literature as inhibitors of other Cas3 variants from distinct bacterial organisms, they found two, AcrIC8 and AcrIC9, with a strong cross-reactive effect against Neisseria Cas3. Using genetic and biochemical studies at UM and cryogenic electron microscopy analyses at Cornell, they determined the mechanism of action and structure of AcrlC8 and AcrlC9 at the molecular level. Both proteins prevent the CRISPR-Cas3 machine from binding to its DNA target site, but by slightly different mechanisms. Finally, the team provided key proof-of-concept that each of these anti-CRISPR proteins can act as a switch for CRISPR-Cas3 in human cells. They can almost completely block two versions of CRISPR-Cas3 technologies, one for deletion of important genomes and the other for gene activation, making them the first switches developed for any CRISPR-Cas3 gene editor.
Researchers developed an RNA-based switch, the pA regulator system, to control gene expression in mammalian cells by modulating synthetic polyA signal cleavage, offering a novel approach for gene therapy applications.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Genetic control in mammalian cells is essential for the development of safe and effective gene therapies. Current methods are associated with certain drawbacks, such as undesirable immunological responses, limited efficacy and overexpression of therapeutic genes. Current gene transfer technologies, such as adeno-associated viruses (AAVs), have difficulty achieving conditional and reversible gene control. Toxic ligands, leakage and high ligand concentrations, as well as small dynamic range are some of the limitations associated with current RNA-based systems. In a recent study researchers describe the pA regulatory system, inserted into cells by CRISPR-Cas9, based on a ribonucleic acid (RNA)-based switch to regulate mammalian gene expression by modulating the cleavage of a synthetic polyA signal (PAS) at a transgenic 5' untranslated region. (UTR). This technique differs from traditional riboswitch systems in that the PAS is present in the 5' UTR, combines the effects of numerous aptamers and uses two processes of Tc binding and alternative splicing. However, the new system can only use Tc as an inducing ligand, which cannot effectively penetrate all body tissues.
Utilizing CRISPR screening, the deubiquitinase ATXN3 has been identified as a key regulator of PD-L1 transcription in tumor cells, a critical factor in tumor immune evasion.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Using CRISPR screening, the deubiquitinase ATXN3 was identified as a key regulator of PD-L1 transcription in tumor cells, a critical factor in tumor immune evasion. In this study, researchers transfected a targeted library of all 96 members of the mammalian deubiquitinase family into melanoma cells, then sorted the cells according to low and high PD-L1 expression to identify the regulators. ATXN3 was found to positively influence PD-L1 transcription, helping tumor cells to evade the immune system. This new insight represents a promising target for improving the efficacy of antitumor immunotherapy by blocking checkpoints, potentially transforming cancer treatment strategies. The study also highlights the broader role of ATXN3 in regulating tumor microenvironmental responses to hypoxia and inflammation, opening up new avenues for cancer research and treatment.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Researchers explored the impact of dietary-derived trans-vaccenic acid (TVA) on effector cytotoxic T lymphocyte functions and anti-tumor immunity in in vivo settings using CRISPR. Overall, the results of the study showed that dietary trans-vaccenic acid enhances effector cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity and anti-tumor immunity in in vivo contexts. In contrast to intra-organism SCFA derived from intestinal microbes functioning as agonists of the G protein-coupled immunoregulatory receptor 43 (GPR43), extra-organism VAT reprogrammed CD8+ T lymphocytes by extrinsic regulation to inactivate GPR43. The results of the study contribute to a better understanding of the molecular links between nutrition and human pathophysiology, with implications for future research into the function of circulating nutrients in health and disease. Further research is needed to improve understanding of the effector pathways downstream of GPR43 and elucidate the underlying processes.
Immunotherapy using modified chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells has greatly improved survival rates for pediatric patients with relapsed and recurrent leukemia.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Solid tumors generate anti-immune signals that deactivate CAR T cells, making treatment less effective. To solve this problem, scientists have combined CAR T cells with cytokine injection, which can cause significant unintended toxicities. Researchers replaced the extracellular domain of various cytokine receptors with leucine zippers to create constitutively active receptors. CAR T cells expressing one of these chimeric cytokine receptors had superior antitumor activity against several types of cancer in cell lines and mouse models compared with conventional CAR T cells. Although chimeric cytokine receptors give a constant "on" signal to CAR T cells, they do not induce non-specific proliferation of CAR T cells. The system thus limits the effect of cytokine signaling to modified cells only, reduces the risk of cytokine-related toxicity, and provides a signal that these CAR T cells should function effectively in a suppressive tumor microenvironment. 
runtzwraps's curator insight,
December 18, 2023 4:42 PM
https://runtzwrapz.com If you have any questions about our return coverage, please Really don't hesitate to Call us. We worth your business and take pleasure in the opportunity to serve you. Some are aged with strawberries to find the strawberry flavor, others are aged with vanilla, bourbon and cocoa to have the accurate vanilla taste we all appreciate. You may check out Agave that's aged with sweet honey and maple syrup. https://runtzwrapz.com https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/big-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-agave-runtz-wrap-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-split-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-berry-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-cake-mix-runtz-online https://runtzwrapz.com https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/big-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-agave-runtz-wrap-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-split-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-berry-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-cake-mix-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-frosties-runtz-onlne/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-runtz-weed-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-sharklato-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-vanilla-cream-runtz-wraps/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/cbd-gummy-bears-100mg/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/ed-bills-lollipop-40mg/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-fresh-strawberry-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/mango-kush-strain/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/motorbreath-strain-near-me/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-natural-runtz-wraps-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/white-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com If you have any questions about our return coverage, please Really don't hesitate to Call us. We worth your business and take pleasure in the opportunity to serve you. Some are aged with strawberries to find the strawberry flavor, others are aged with vanilla, bourbon and cocoa to have the accurate vanilla taste we all appreciate. You may check out Agave that's aged with sweet honey and maple syrup. https://runtzwrapz.com https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/big-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-agave-runtz-wrap-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-split-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-berry-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-cake-mix-runtz-online https://runtzwrapz.com https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/big-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-agave-runtz-wrap-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-split-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-berry-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-cake-mix-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-frosties-runtz-onlne/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-runtz-weed-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-sharklato-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-vanilla-cream-runtz-wraps/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/cbd-gummy-bears-100mg/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/ed-bills-lollipop-40mg/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-fresh-strawberry-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/mango-kush-strain/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/motorbreath-strain-near-me/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-natural-runtz-wraps-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/white-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com If you have any questions about our return coverage, please Really don't hesitate to Call us. We worth your business and take pleasure in the opportunity to serve you. Some are aged with strawberries to find the strawberry flavor, others are aged with vanilla, bourbon and cocoa to have the accurate vanilla taste we all appreciate. You may check out Agave that's aged with sweet honey and maple syrup. https://runtzwrapz.com https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/big-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-agave-runtz-wrap-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-split-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-berry-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-cake-mix-runtz-online https://runtzwrapz.com https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/big-runtz-strain-for-sale/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-agave-runtz-wrap-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-banana-split-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-berry-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-cake-mix-runtz-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-frosties-runtz-onlne/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-runtz-weed-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-sharklato-runtz/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-vanilla-cream-runtz-wraps/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/cbd-gummy-bears-100mg/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/ed-bills-lollipop-40mg/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-fresh-strawberry-runtz-wrap/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/mango-kush-strain/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/motorbreath-strain-near-me/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/buy-natural-runtz-wraps-online/ https://runtzwrapz.com/product/white-runtz-strain-for-sale/
|
Mayo Clinic scientists have developed an immunotherapy strategy that potentially lays the groundwork for treating a spectrum of autoimmune diseases.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Graft-versus-host disease occurs when a donor's cells attack the recipient's tissues, usually following a bone marrow or stem cell transplant. In a recent study, a new technique involving the combination of Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs) with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs), resulting in modified stem cells known as CAR-MSCs, was used to specifically target a protein linked to graft-versus-host disease, but also to inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. In mouse models, when stimulated by the specific protein for which they were designed, CAR-MSCs showed an enhanced ability to reach the inflamed area, better control inflammation and improve outcome and survival. This was mediated by a change in the genetic signature of CAR-MSCs, the proteins they released and receptor expression. These preliminary results pave the way for future applications of this technology, paving the way for improving the versatility of the therapy to treat various diseases across the autoimmune spectrum.
From
www
Treatment with a next-generation CAR T-cell agent displayed early efficacy in a small group of patients with glioblastoma.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
CARv3-TEAM-E T cells are CAR T cells targeting EGFR variant III tumor-specific antigen (EGFRvIII) in addition to wild-type EGFR. According to the results of the phase 1 INCIPIENT trial (NCT05660369) published in the New England Journal of Medicine, preliminary results in humans demonstrated that all 3 glioblastoma patients treated with CARv3-TEAM-E T cells between March 2023 and July 2023 showed dramatic and rapid radiographic regression of their tumors within days of receiving CARv3-TEAM-E T cells via a single intraventricular infusion. Responses were transient in 2 of the patients, however 1 patient, a 72-year-old man, showed an 18.5% decrease in tumor cross-sectional area on day 2 after receiving a single infusion of 10 x 106 CAR-positive CARv3-TEAM-E T cells. Moreover, 69 days after infusion, tumor cross-sectional area had decreased by a further 60.7% from baseline; the response was sustained and continued to improve at the last assessment, which took place more than 150 days after infusion.
Targeting two brain tumor-associated proteins-;rather than one-;with CAR T cell therapy shows promise as a strategy for reducing solid tumor growth in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (GBM), an aggressive form of brain cancer, according to early results from the first six patients treated in an ongoing Phase I clinical trial led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine's Abramson Cancer Center.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive type of cancerous brain tumor in adults. People with GBM generally expect to live 12 to 18 months after diagnosis. Despite decades of research, there is no known cure for GBM, and treatments have only a limited effect on extending an individual's life expectancy. However, researchers have tested a technology that delivers CAR-T cells targeting two proteins commonly found in brain tumors: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), estimated to be present in 60% of all GBMs, and interleukin-13 receptor alpha 2 (IL13Rα2), which is expressed in over 75% of GBMs. While CAR-T cell therapy for blood cancers is usually administered intravenously, the researchers administered these dual-targeted CAR-T cells intrathecally, by injection into the cerebrospinal fluid, so that the modified cells could reach the tumors more directly in the brain. Magnetic Resonance Imaging scans taken 24 to 48 hours after administration of dual-targeted CAR-T cells targeting EGFR and IL13Rα2 revealed a reduction in tumor size in all six patients, and these reductions were maintained up to several months later in a subgroup of patients.
From
www
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) reporters are commonly used in the final stages of nucleic acid amplification tests to indicate the presence of nucleic acid targets, where fluorescence is restored by nucleases that cleave the FRET reporters. However, the need for dual labelling and purification during manufacturing contributes to the high cost of FRET reporters. Here we demonstrate a low-cost silver nanocluster reporter that does not rely on FRET as the on/off switching mechanism, but rather on a cluster transformation process that leads to fluorescence color change upon nuclease digestion. Notably, a 90 nm red shift in emission is observed upon reporter cleavage, a result unattainable by a simple donor-quencher FRET reporter. Electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry results suggest that the stoichiometric change of the silver nanoclusters from Ag13 (in the intact DNA host) to Ag10 (in the fragments) is probably responsible for the emission colour change observed after reporter digestion. Our results demonstrate that DNA-templated silver nanocluster probes can be versatile reporters for detecting nuclease activities and provide insights into the interactions between nucleases and metallo-DNA nanomaterials. Here the authors present a non-FRET DNA-templated silver nanocluster probe that exhibits a distinct colour switch from green to red upon nuclease digestion, visible under UV excitation, offering a low-cost, effective alternative to fluorescent reporters for detecting nuclease activities.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
A new tool could reduce the cost of diagnosing infectious diseases. Researchers have developed a new, less expensive means of detecting nuclease digestion, one of the critical steps in many nucleic acid detection applications, such as those used to identify COVID-19 and other infectious diseases. A new study published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology shows that this inexpensive tool, called Subak, is effective in determining when nucleic acid cleavage occurs, which happens when an enzyme called nuclease breaks down nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA, into smaller fragments. The traditional method for identifying nuclease activity, the Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) probe, is 62 times more expensive to produce than the Subak reporter.
Siteman Cancer Center, based at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is one of the first centers nationwide to offer a newly approved cell-based immunotherapy that targets melanoma.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Following the approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), doctors at the University of Washington's Siteman Cancer Center will administer tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy to treat certain adult patients with metastatic melanoma, an aggressive skin cancer that has spread to other areas of the body. The treatment is intended for patients with metastatic melanoma that cannot be treated by surgery and has continued to grow and spread despite having already been heavily treated with other approved strategies, including chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors. The first centers to administer TIL therapy are those with extensive expertise in treating patients with cellular immunotherapies, such as CAR-T cell therapy for blood cancers. For the therapy, doctors at an approved treatment center take a sample of the tumor and send the tissue to an Iovance manufacturing facility, where tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are isolated from the tumor and then expanded outside the body. This TIL therapy cell product is then cryopreserved and returned to the patient. When returned to the patient's body via intravenous infusion, the tumor-specific T cells, now numbering in the billions, are much more effective at killing tumor cells throughout the body.
Review synthesizes research on NK cells' role in cancer immunity and their potential in therapeutics through bioengineering, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and cell engagers, highlighting ongoing preclinical and clinical trials.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, researchers have compiled the available literature on natural killer (NK) cells, innate immune cells involved in the recognition and elimination of cells in distress, particularly virus-infected cells and tumors. They focus on reviewing current preclinical and clinical research in the field of NK therapies, primarily elucidating the role of NK cells in cancer immunity. They also explore the potential of bioengineering approaches to harness NK cells via the development of genetically modified NK cells, immune checkpoint inhibitors and cell engagement agents. The study reveals that, despite less than two decades of research in the field, NK cells are emerging as a safe, practical and potentially widely accessible means of clinical therapy, particularly antitumor. Although challenges exist in the adoption of NK cell therapies by conventional medicine, studies aimed at overcoming these challenges are already underway, bringing the future of clinical NK cell interventions closer than ever.
This study is led by Prof. Xianqun Fan (Department of Ophthalmology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Affiliated Ninth People's Hospital).
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
In a review, researchers detail the development history of Principal Editing (PE), the latest evolution of CRISPR-Cas-based technologies. PE was proposed by a team of researchers in 2019, which is characterized by the absence of double-strand breaks (DSBs) or homology sequence patterns with variable application scenarios, including point mutations as well as insertions or deletions. The PE system consists of two parts: the master editors (PEs) and the master editing guide RNA (pegRNA). This PE system has developed and progressed rapidly over the last four years, with versatile advances in its architecture to increase editing efficiency, targeting and specificity, including a new pegRNA design, PE modification and improved delivery. Moreover, despite its relatively recent inception, PE has been widely applied to correct pathological mutations associated with genetic diseases, both in vitro and in vivo , presenting great potential for advancing the field of gene therapy from bench to bedside.
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, or CAR T, has dramatically improved the treatment of certain blood cancers. Initially approved for patients who had failed multiple lines of therapy, clinical trials have shown CAR T can be used as an earlier treatment option.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Axi-cel CAR T therapy targets the CD19 molecule on large B-cell lymphoma cells. The ZUMA-7 trial demonstrated that axi-cel reduced the risk of disease progression, need for retreatment or death by 60% compared with standard therapy. Despite these positive results in terms of event-free survival and overall survival, some patients did not respond well to treatment or relapsed rapidly after treatment. Researchers analyzed tumor gene expression patterns from patient samples and determined that a B-cell gene expression signature and CD19 protein expression were significantly associated with improved event-free survival for patients treated with axi-cel but not with standard therapy. Patients with lower tumor cell levels of CD19 showed gene expression patterns associated with immunosuppression. These observations suggest that the tumor immune environment may play an important role in regulating axi-cel treatment and outcome. Furthermore, biomarkers associated with improved axi-cel treatment outcomes decreased as patients received more treatments, suggesting that receiving axi-cel as part of earlier treatment lines is essential to ensure better patient outcomes.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Researchers have reported promising results in a Phase I/II trial involving 37 patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies who were treated with a cord blood-derived natural killer (NK) chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), a cell therapy targeting CD19. Results showed an overall response (OR) rate of 48.6% 100 days after treatment, with one-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates of 32% and 68%, respectively. The trial reported an excellent safety profile, with no cases of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity or graft-versus-host disease. Another key finding of the trial was the importance of allogeneic cord blood donor selection criteria in the manufacture of CAR NK cells. Cord blood units cryopreserved within 24 hours of collection and those with a low content of nucleated red blood cells were associated with significantly better results. CAR NK cells generated from these units resulted in a one-year PFS rate of 69% and an OS rate of 94%, compared with 5% and 48%, respectively, for units with higher nucleated red cell content or longer collection to cryopreservation times.
At EPFL's School of Engineering, Professor Li Tang's Laboratory of Biomaterials for Immunoengineering has made significant strides in cancer treatment research.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Traditional CAR-T cells, while effective against liquid cancers, face challenges in solid tumors: the cells wear out and ultimately fail to destroy the cancer completely. Ground-breaking research is providing an innovative approach to this challenge. Researchers are introducing CAR-T cells that excrete the IL-10 molecule. In other words, the cell has been designed to produce its own "drug" to stay healthy in the tumor's hostile environment. In the laboratory, this innovative CAR-T therapy systematically eradicated cancerous tumors in mouse models. What's more, in ongoing clinical trials, eleven patients have appeared to achieve complete remission with this treatment, representing a 100% success rate to date. Notably, the evidence from the laboratory study suggests the long-term efficacy of the therapy, and indicates that its manufacture could be both faster and more cost-effective than current methods
The recent publication in Science by Mogila, Tamulaitiene et al. represents a continuation of the successful scientific research conducted by Gintautas Tamulaitis' group.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
In a recent study published in Science, researchers characterized a new family of effector proteins, named Cami1, using bioinformatics, biochemical and structural studies. They showed that when a virus attacks a bacterium, CRISPR-Cas10 signaling molecules activate Cami1, a ribosome-dependent ribonuclease. Activated Cami1 cleaves mRNAs involved in protein synthesis, inhibiting cell growth. This saves resources and prevents the production of viral proteins. Cami1's interaction with a specialized ribosomal structure, called a ribosomal stalk, is necessary for its entry into the protein synthesis center. Interestingly, the same capture mechanism to bind the ribosome is used by plant antiviral proteins that also inactivate ribosomes. This discovery has unveiled an additional layer of the CRISPR-Cas antiviral defense system and demonstrated a common antiviral strategy shared between eukaryotes and bacteria. Knowledge of our characterized Cami1 proteins will contribute to the development of new molecular tools in biotechnology and therapy
The gene-editing technology CRISPR shows early promise as a therapeutic strategy for the aggressive and difficult-to-treat brain cancer known as primary glioblastoma, according to findings of a new study from Gladstone Institutes.
BigField GEG Tech's insight:
Glioblastoma is the most common fatal brain cancer, and patients still lack good treatment options. Patients typically receive chemotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery, but most relapse within a few months. However, CRISPR looks very promising as a therapeutic strategy for the aggressive and difficult-to-treat brain cancer known as primary glioblastoma, according to the results of a new study from the Gladstone Institutes. Using computational methods to analyze entire cancer cell genomes, the team dove deep into non-coding DNA to identify the repetitive code they all shared, even if they harbored a different variety of mutations. The researchers then programmed CRISPR to focus on repetitive DNA sequences present only in recurrent tumor cells to destroy these cells. Working with cell lines from a patient whose glioblastoma had recurred after previous treatments, the team used CRISPR to destroy tumor cells while sparing healthy cells. |



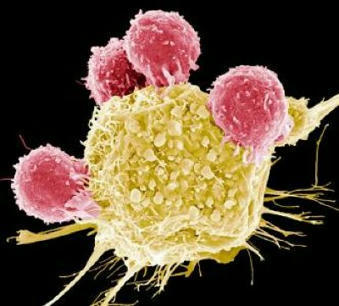















Keeping cells active long enough to eliminate cancer has proved difficult, particularly in solid tumors such as those of the breast and lung. Scientists are therefore looking for better ways to help CAR T cells multiply faster and last longer in the body. To this end, researchers compared samples of CAR T cells used to treat people with leukemia. They analyzed the role of cellular proteins that regulate gene activity and serve as master switches in T cells. They discovered a set of 41 genes that were more active in CAR T cells associated with a good response to treatment than in cells associated with a poor response. All 41 genes appeared to be regulated by a master protein called FOXO1. The researchers then engineered the CAR T cells to produce more FOXO1 than usual. Gene activity in these cells began to resemble that of memory T stem cells, which recognize cancer and respond quickly to it. The researchers then injected the modified cells into mice with different types of cancer. Extra FOXO1 enabled the CAR T cells to better reduce both solid tumors and blood cancers. Moreover, another team also reached the same conclusion by working on gene activity analysis in CAR T cells and also discovered that IL-15 activated genes associated with FOXO1.